The Schmid fall risk assessment tool is a crucial instrument used in acute care settings to identify patients at risk of falling. It helps healthcare professionals proactively implement preventative measures to ensure patient safety and minimize fall-related injuries. Understanding how to use and interpret the Schmid fall risk assessment tool is essential for providing effective care in the fast-paced environment of acute care.
Understanding the Schmid Fall Risk Assessment Tool
The Schmid fall risk assessment tool is a relatively simple and quick method to assess a patient’s fall risk. It takes into account various factors that contribute to falls, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation. These factors can include previous falls, mobility limitations, cognitive impairments, medication side effects, and environmental hazards. The tool typically uses a points-based system where higher scores indicate a greater risk of falling.
Why Use the Schmid Fall Risk Assessment Tool in Acute Care?
Acute care environments are often characterized by rapid patient turnover, frequent changes in medication regimens, and a high prevalence of acute illnesses. These factors can significantly increase a patient’s susceptibility to falls. The Schmid tool allows healthcare professionals to quickly identify high-risk individuals and implement appropriate interventions.
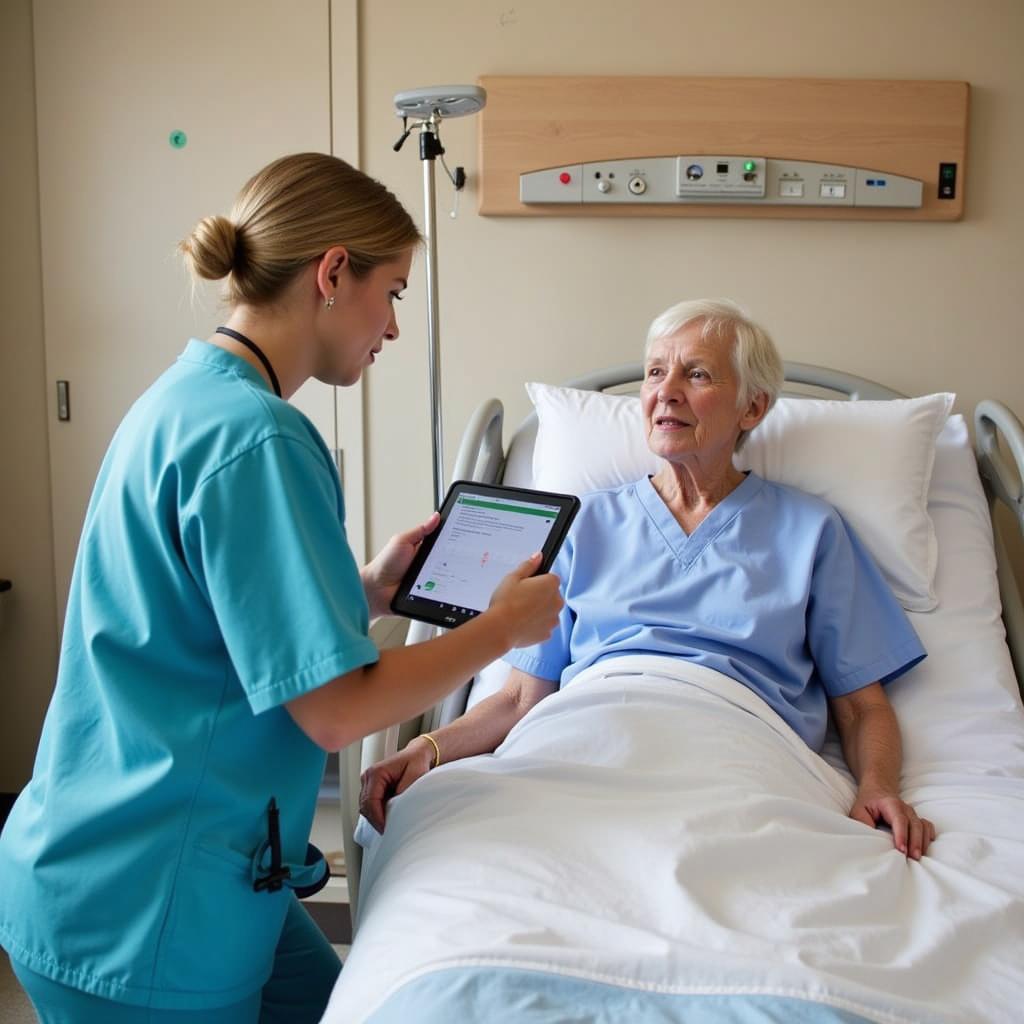 Nurse using the Schmid fall risk assessment tool on a patient
Nurse using the Schmid fall risk assessment tool on a patient
The tool helps standardize fall risk assessment, ensuring consistency in patient care and facilitating communication among healthcare team members. This consistent approach contributes to a safer environment for patients and reduces the incidence of falls. Early identification of fall risk also helps prevent potential complications associated with falls, such as fractures, head injuries, and prolonged hospital stays.
Key Components of the Schmid Fall Risk Assessment Tool
The specific components of the Schmid fall risk assessment tool may vary slightly depending on the institution or version being used. However, common elements typically include:
- History of falls: Previous falls are a strong predictor of future falls.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as sedatives and diuretics, can increase fall risk.
- Mobility: Assesses the patient’s ability to ambulate and transfer.
- Cognitive status: Cognitive impairment can contribute to confusion and disorientation, increasing fall risk.
- Sensory impairments: Visual or auditory impairments can make it difficult for patients to navigate their surroundings safely.
- Elimination: Frequent or urgent bathroom needs can lead to rushed movements and falls.
Interpreting the Schmid Fall Risk Assessment Score
After completing the assessment, the scores are tallied to determine the patient’s fall risk level. Each institution typically has specific protocols based on the score. These protocols may include increased monitoring, assistance with ambulation, environmental modifications, and patient education.
 Chart displaying the interpretation of the Schmid fall risk assessment score
Chart displaying the interpretation of the Schmid fall risk assessment score
“Regularly assessing fall risk and implementing appropriate interventions are crucial for ensuring patient safety in acute care settings,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a geriatric specialist at Chicago General Hospital. “The Schmid tool provides a valuable framework for this process.”
Implementing Fall Prevention Strategies Based on the Schmid Assessment
The Schmid fall risk assessment tool is not just about identifying risk; it’s about guiding intervention. Based on the assessment results, healthcare professionals can implement a variety of fall prevention strategies, such as:
- Educating patients and families: Providing information about fall risks and prevention measures.
- Modifying the environment: Removing clutter, ensuring adequate lighting, and providing assistive devices.
- Adjusting medications: Reviewing medications and making adjustments as needed to minimize fall risk.
- Providing assistance with mobility: Offering assistance with ambulation and transfers.
- Implementing regular toileting schedules: Assisting patients with toileting needs to prevent rushed movements.
Best Practices for Using the Schmid Fall Risk Assessment Tool
To ensure the effectiveness of the Schmid tool, healthcare professionals should be properly trained on its use and interpretation. Regular reassessments are also essential, as a patient’s fall risk can change rapidly in the acute care setting.
 Hospital room with fall prevention measures in place
Hospital room with fall prevention measures in place
“Using the Schmid tool consistently and documenting the results are critical for effective fall prevention,” adds Dr. Michael Davis, a registered nurse with over 15 years of experience in acute care. “This allows for better communication among healthcare team members and ensures that appropriate interventions are in place.”
Conclusion
The Schmid fall risk assessment tool is a valuable resource in acute care settings for identifying and managing fall risk. By understanding and applying this tool effectively, healthcare professionals can significantly improve patient safety and reduce the incidence of falls and related injuries. Consistent use of the Schmid fall risk assessment tool, combined with appropriate interventions, is essential for creating a safer environment for patients in acute care.
FAQ
- How often should the Schmid fall risk assessment be performed?
- What are the limitations of the Schmid fall risk assessment tool?
- Are there other fall risk assessment tools used in acute care?
- How can I access training on using the Schmid fall risk assessment tool?
- What are the common causes of falls in acute care settings?
- What are the consequences of falls in older adults?
- How can families be involved in fall prevention efforts?
If you need further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 910 Cedar Lane, Chicago, IL 60605, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.

Leave a Reply