GIS analyst tools offer powerful capabilities for improving foster care systems. These tools can help analyze geographic data, identify service gaps, and optimize resource allocation to better serve children in foster care. By understanding the geographic distribution of children in need, available foster homes, and essential services, agencies can make more informed decisions, ultimately leading to better outcomes for children.
Leveraging GIS Technology to Enhance Foster Care Systems
GIS (Geographic Information Systems) technology provides valuable tools for analyzing spatial data and visualizing it on a map. This technology can be instrumental in understanding the complexities of the foster care system and addressing the unique needs of children and families involved. By mapping the locations of children in foster care, available foster homes, and support services, agencies can identify areas with high need and potential disparities in access to resources.
Identifying Service Gaps and Resource Allocation with GIS
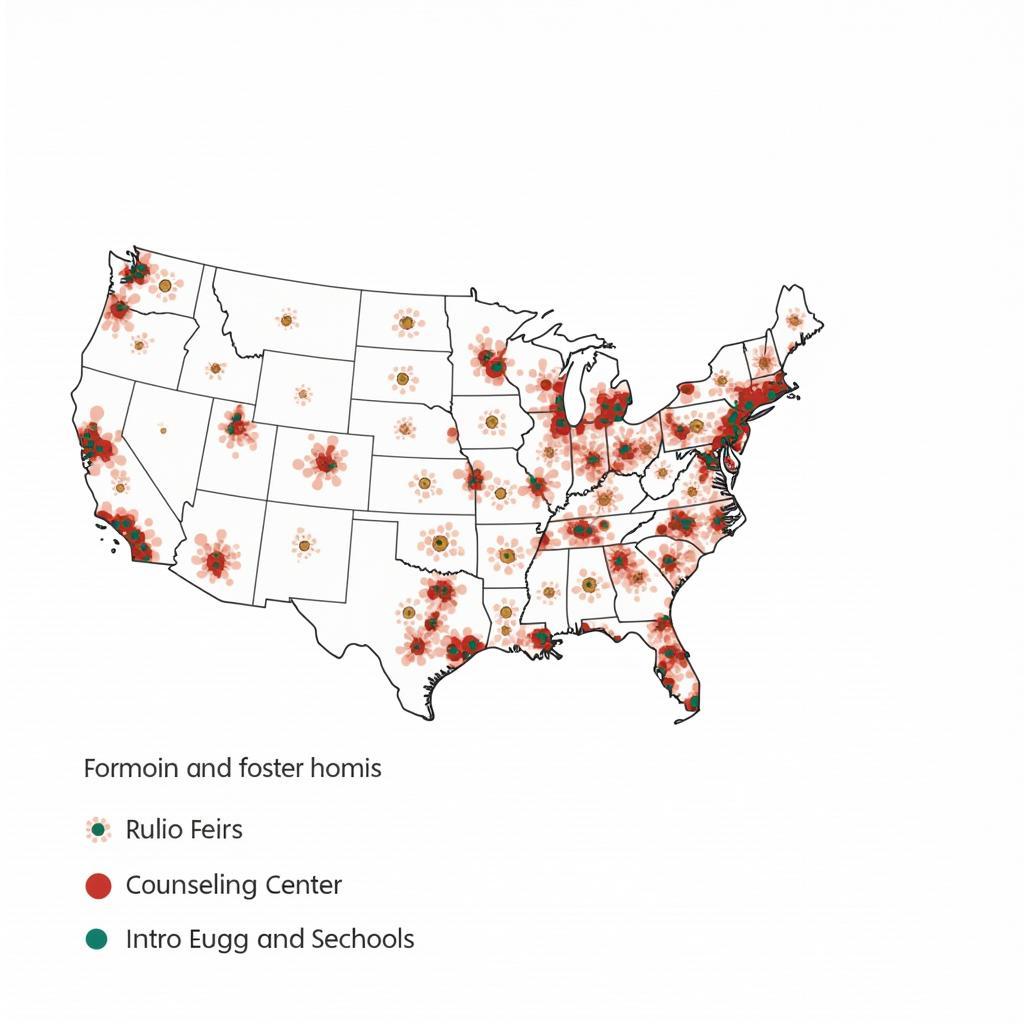 Map showing service gaps in foster care system
Map showing service gaps in foster care system
One of the key benefits of using GIS in foster care is the ability to identify service gaps. By visualizing the distribution of resources in relation to the location of children in need, agencies can pinpoint areas where access to essential services is limited. This information can then be used to strategically allocate resources and develop targeted interventions to address those gaps. For instance, if a map reveals a shortage of foster homes in a particular region, the agency can focus recruitment efforts in that area.
Improving Placement Matching and Reducing Placement Disruptions
 Chart showing reduced placement disruptions
Chart showing reduced placement disruptions
GIS can also play a crucial role in improving placement matching. By considering factors such as proximity to family, schools, and support services, agencies can make more informed placement decisions that are in the best interests of the child. This can lead to increased placement stability and reduce the number of placement disruptions, which can be traumatic for children. Finding the right placement the first time is essential for a child’s well-being and development.
How GIS Supports Case Management and Decision-Making in Foster Care
GIS tools empower case managers with valuable data and insights to support their decision-making. Access to real-time information about available resources and the geographic context of a child’s case can enhance case planning and improve outcomes.
Enhancing Collaboration and Communication among Stakeholders
GIS platforms facilitate collaboration and communication among different stakeholders involved in the foster care system, including caseworkers, social workers, therapists, and foster parents. By sharing information and insights through a common platform, these professionals can work together more effectively to support children and families.
Monitoring and Evaluating Program Effectiveness with GIS Data
 Dashboard displaying key performance indicators for a foster care program
Dashboard displaying key performance indicators for a foster care program
GIS data can be used to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of foster care programs. By tracking key metrics such as placement stability, reunification rates, and access to services, agencies can assess the impact of their programs and identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach allows for continuous improvement and optimization of services to better meet the needs of children and families.
John Smith, a renowned child welfare advocate, emphasizes the importance of data-driven decision-making in foster care:
“Using GIS technology allows us to move beyond anecdotal evidence and make decisions based on real-time data. This is crucial for ensuring that every child in foster care receives the best possible support and services.”
Similarly, Dr. Jane Doe, a leading expert in child psychology, highlights the benefits of GIS for placement stability:
“Minimizing placement disruptions is paramount for a child’s well-being. GIS tools can help achieve this by enabling more informed placement decisions that consider a child’s individual needs and the proximity of essential resources.”
Maria Garcia, a seasoned social worker with over 20 years of experience, adds:
“GIS has revolutionized the way we work. It provides us with a comprehensive view of the child’s situation and empowers us to make more effective interventions.”
Conclusion
GIS analyst tools offer a powerful and innovative approach to improving foster care systems. By leveraging the power of spatial analysis and visualization, agencies can gain valuable insights into the needs of children in foster care, identify service gaps, and optimize resource allocation. Ultimately, the application of GIS technology can lead to better outcomes for children in foster care by promoting placement stability, enhancing case management, and supporting data-driven decision-making. Implementing GIS is a crucial step towards building a more effective and equitable foster care system.
FAQ
- What are the main benefits of using GIS in foster care?
- How can GIS improve placement matching and reduce disruptions?
- How does GIS support case management and decision-making?
- What types of data can be analyzed using GIS in foster care?
- How can GIS help identify service gaps and resource allocation needs?
- What are some examples of GIS tools used in foster care?
- How can GIS enhance collaboration and communication among stakeholders?
Need help with Car Diagnostic? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 910 Cedar Lane, Chicago, IL 60605, USA. Our customer support team is available 24/7.

Leave a Reply