The modern vehicle is a complex network of electronic systems controlling everything from engine performance to safety features. Understanding the Types Of Car Diagnostic Tools available is crucial for mechanics, technicians, and even car enthusiasts to effectively diagnose and repair issues. This guide delves into the diverse world of car diagnostic tools, providing valuable insights into their functionalities, advantages, and limitations.
What are Car Diagnostic Tools?
Car diagnostic tools are sophisticated instruments used to interface with a vehicle’s onboard computer system, the Engine Control Unit (ECU). This connection allows for the retrieval of valuable data about the vehicle’s health, performance, and any potential problems. By interpreting the data provided by these tools, mechanics can pinpoint the root cause of malfunctions, streamlining the repair process.
Different Types of Car Diagnostic Tools
The evolution of automotive technology has led to a wide array of diagnostic tools, each with specific capabilities. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
1. OBD2 Scanners: The Foundation of Diagnostics
OBD2 scanners are the cornerstone of car diagnostics, offering a gateway to the vehicle’s ECU. They retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), which are standardized codes that indicate specific malfunctions within the vehicle’s systems.
Types of OBD2 Scanners:
- Basic Code Readers: Entry-level devices primarily designed to read and clear DTCs.
- Advanced Code Readers: Offer additional features like live data streaming, freeze frame data, and the ability to access manufacturer-specific codes.
- Professional Scan Tools: Comprehensive tools used by mechanics and technicians, providing advanced functionalities like bi-directional control, programming, and coding capabilities.
2. Oscilloscopes: Analyzing Electrical Signals
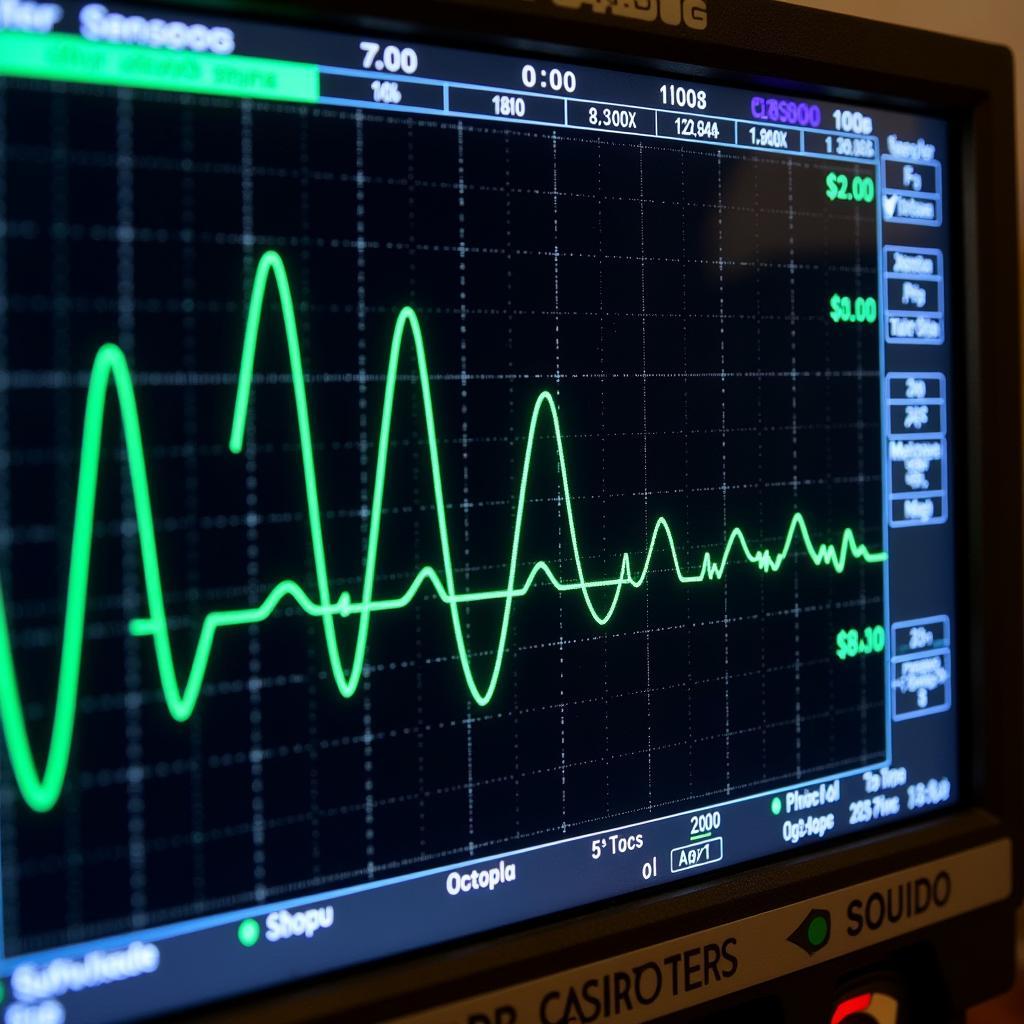 Automotive Oscilloscope Displaying Signal Patterns
Automotive Oscilloscope Displaying Signal Patterns
Oscilloscopes are powerful tools that visualize electrical signals within a vehicle’s various systems. Mechanics use oscilloscopes to diagnose complex electrical issues that may not trigger DTCs, such as:
- Sensor malfunctions: Identifying faulty signals from sensors like crankshaft position sensors or oxygen sensors.
- Wiring problems: Detecting short circuits, open circuits, or high resistance in wiring harnesses.
- Actuator performance: Analyzing the electrical signals sent to actuators like fuel injectors or ignition coils.
3. Pressure Gauges: Monitoring Vital Fluids
Pressure gauges are essential for monitoring the pressure of critical fluids in a vehicle. They provide crucial insights into the health of systems like:
- Engine Oil Pressure: Low or fluctuating oil pressure can indicate severe engine problems.
- Fuel Pressure: Diagnosing fuel delivery issues like clogged fuel filters or malfunctioning fuel pumps.
- Coolant Pressure: Monitoring the cooling system’s pressure to prevent overheating and head gasket failures.
4. Vacuum Gauges: Unveiling Engine Health
Vacuum gauges measure the vacuum pressure within a vehicle’s intake manifold. This pressure reading provides valuable information about the engine’s overall health, including:
- Engine vacuum leaks: Identifying leaks in the intake manifold, vacuum hoses, or other components.
- Valve timing issues: Detecting problems with valve timing, such as a worn timing belt or chain.
- Ignition system health: Assessing the condition of spark plugs, ignition wires, and the distributor (in older vehicles).
5. Battery Testers: Ensuring Electrical System Integrity
Battery testers are crucial for determining the health and charge level of a vehicle’s battery. They can perform various tests, such as:
- Battery voltage test: Measuring the battery’s voltage to determine its state of charge.
- Battery load test: Simulating a heavy electrical load to assess the battery’s ability to provide sufficient current.
- Alternator test: Checking the alternator’s output voltage and current to ensure it’s charging the battery properly.
Choosing the Right Car Diagnostic Tools
Selecting the appropriate car diagnostic tools depends on several factors, including:
- Level of Expertise: Basic code readers are suitable for DIY enthusiasts, while professional mechanics require advanced scan tools.
- Vehicle Make and Model: Some tools are designed for specific vehicle manufacturers or models.
- Budget: The price of diagnostic tools varies widely, from affordable code readers to high-end professional scanners.
Conclusion: Empowering Automotive Diagnostics
Understanding the different types of car diagnostic tools empowers mechanics, technicians, and car enthusiasts to effectively diagnose and repair vehicle problems. From basic code readers to sophisticated oscilloscopes, these tools provide the necessary insights to keep vehicles running smoothly. By embracing the power of diagnostic technology, automotive professionals can enhance their troubleshooting capabilities and ensure optimal vehicle performance.

Leave a Reply