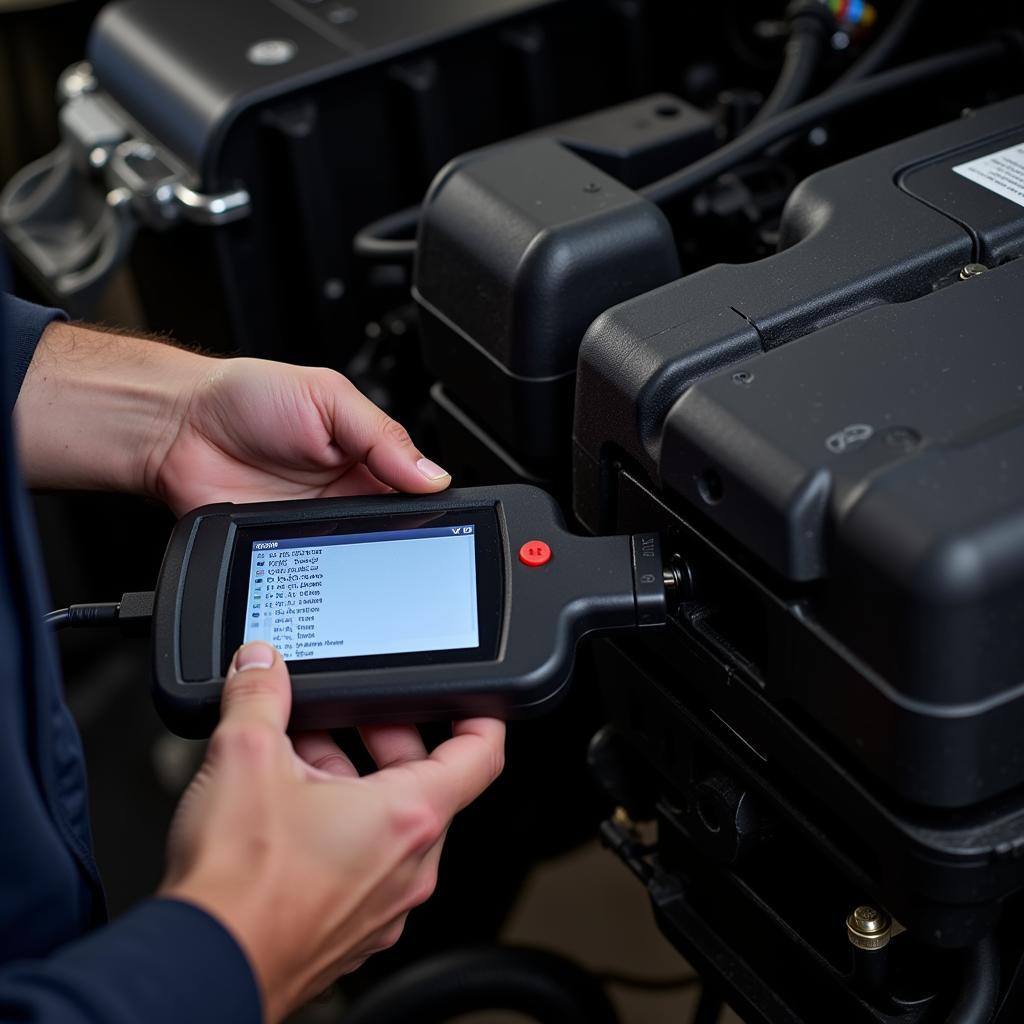
A diagnostic car device has become essential for car owners and mechanics alike. This powerful tool allows you to delve into your vehicle’s computer system, revealing hidden issues and providing valuable data that can streamline repairs, improve performance, and save you time and money in the long run.
Why are Diagnostic Car Devices so Important?
Gone are the days of relying solely on a mechanic’s intuition and experience to diagnose car problems. Modern vehicles are equipped with complex electronic systems that control everything from engine performance to safety features. A diagnostic car device acts as a window into these systems, allowing you to:
-
Read and Clear Trouble Codes: When your car’s “check engine” light illuminates, a trouble code is stored in the vehicle’s computer. A diagnostic device can read these codes, providing valuable insight into the potential issue. Even better, once the problem is resolved, you can use the device to clear the code.
-
Monitor Real-Time Data: Want to know your engine’s coolant temperature, fuel pressure, or oxygen sensor readings? A diagnostic car device can display this information in real time, allowing you to monitor your vehicle’s performance and identify potential problems before they escalate.
-
Customize Vehicle Settings: Some advanced diagnostic car devices allow you to access and modify certain vehicle settings. This might include adjusting shift points, disabling daytime running lights, or even programming new keys.
Types of Diagnostic Car Devices
There is a wide range of diagnostic car devices available, from basic code readers to professional-grade scan tools. Here’s a quick overview:
-
Basic Code Readers: As the name suggests, these devices primarily focus on reading and clearing trouble codes. They are generally the most affordable option and suitable for DIY car owners who want to perform basic diagnostics.
-
OBD-II Scanners: OBD-II scanners offer more advanced features than basic code readers. They can display live data streams, graph sensor readings, and provide more detailed information about the trouble codes.
-
Professional-Grade Scan Tools: Used by mechanics and automotive specialists, these tools offer the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. They can perform advanced functions such as module coding, bi-directional control, and access to manufacturer-specific data.
Choosing the Right Diagnostic Car Device
With so many options available, choosing the right diagnostic car device can seem daunting. Consider these factors to narrow down your choices:
-
Your Budget: Diagnostic devices range in price from under $50 to over $1,000. Set a realistic budget before you start shopping.
-
Your Skill Level: If you’re a DIY beginner, a basic code reader or an OBD-II scanner should suffice. For more advanced users, a professional-grade scan tool might be a worthwhile investment.
-
Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the device you choose is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Most modern cars use the OBD-II standard, but some older vehicles might require specialized adapters or software.
-
Features and Functions: Think about the specific features you need. Do you simply want to read and clear codes, or are you interested in accessing live data, graphing sensor readings, or performing advanced diagnostics?
Conclusion
A diagnostic car device is an invaluable tool for any car owner or mechanic. By giving you access to your vehicle’s inner workings, it empowers you to diagnose problems accurately, monitor performance, and potentially save money on costly repairs. When selecting a device, consider your budget, skill level, and desired features to find the perfect tool for your needs.