Using a scan tool, also known as an OBD2 scanner, is crucial for understanding and fixing car problems. This guide will provide a step-by-step approach to effectively using a scan tool on your car, covering everything from basic code reading to advanced diagnostics.
Modern vehicles are complex machines controlled by a network of computers. When something goes wrong, the car’s computer system stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in its memory. A scan tool allows you to access these codes, understand what they mean, and take the necessary steps to resolve the underlying issue. After reading this article, you’ll be able to confidently diagnose your car’s problems. You can find more information on specific scan tools, such as the Snap-on professional car scan tool, on our website.
Understanding OBD2 and Scan Tools
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that allows a scan tool to communicate with a vehicle’s computer system. All cars manufactured after 1996 in the United States and most cars manufactured after 2001 in other regions are equipped with OBD2. Scan tools, ranging from simple code readers to advanced professional diagnostic tools, plug into the OBD2 port, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
Locating the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is typically a 16-pin trapezoidal connector found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Sometimes, it can be hidden behind a panel or near the steering wheel. Consult your car’s owner manual if you’re having trouble locating it.
Connecting the Scan Tool
Once you’ve found the OBD2 port, turn the ignition key to the “on” position (do not start the engine). Then, plug the scan tool into the OBD2 port. Most scan tools power on automatically when connected.
Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Select the “Read Codes” option on your scan tool. The tool will then retrieve any stored DTCs from the car’s computer. Each DTC is a five-character alphanumeric code. You can then find more information on car scanner tools used with smart phones on DiagFixPro.
What do the Codes Mean?
DTCs are standardized, meaning the same code represents the same problem across different car makes and models. However, the specific causes for a particular DTC can vary. You can usually look up DTC definitions online or in a repair manual.
 Interpreting DTC codes displayed on a car scan tool
Interpreting DTC codes displayed on a car scan tool
Clearing the Codes
After diagnosing and repairing the problem, you can clear the codes using the “Clear Codes” function on your scan tool. This is important for confirming the fix and ensuring the check engine light stays off.
Advanced Scan Tool Functions
Besides reading and clearing codes, more advanced scan tools offer additional functionalities, such as:
- Live Data: View real-time data from various sensors, like engine temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel pressure. This is crucial for diagnosing intermittent problems.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures a snapshot of sensor readings at the moment a code was set, providing valuable clues about the conditions that led to the fault.
- Actuator Tests: Allows you to activate various components, such as fuel injectors or solenoids, to test their functionality.
- Special Functions: Depending on the scan tool and vehicle, access specific functions like resetting oil change lights, performing ABS brake bleeding, or programming keys. DiagFixPro offers resources on how to use car scan tools effectively.
“Using a quality scan tool paired with a comprehensive understanding of your vehicle’s systems can empower you to tackle many repairs yourself,” advises John Miller, a seasoned automotive diagnostician with over 25 years of experience.
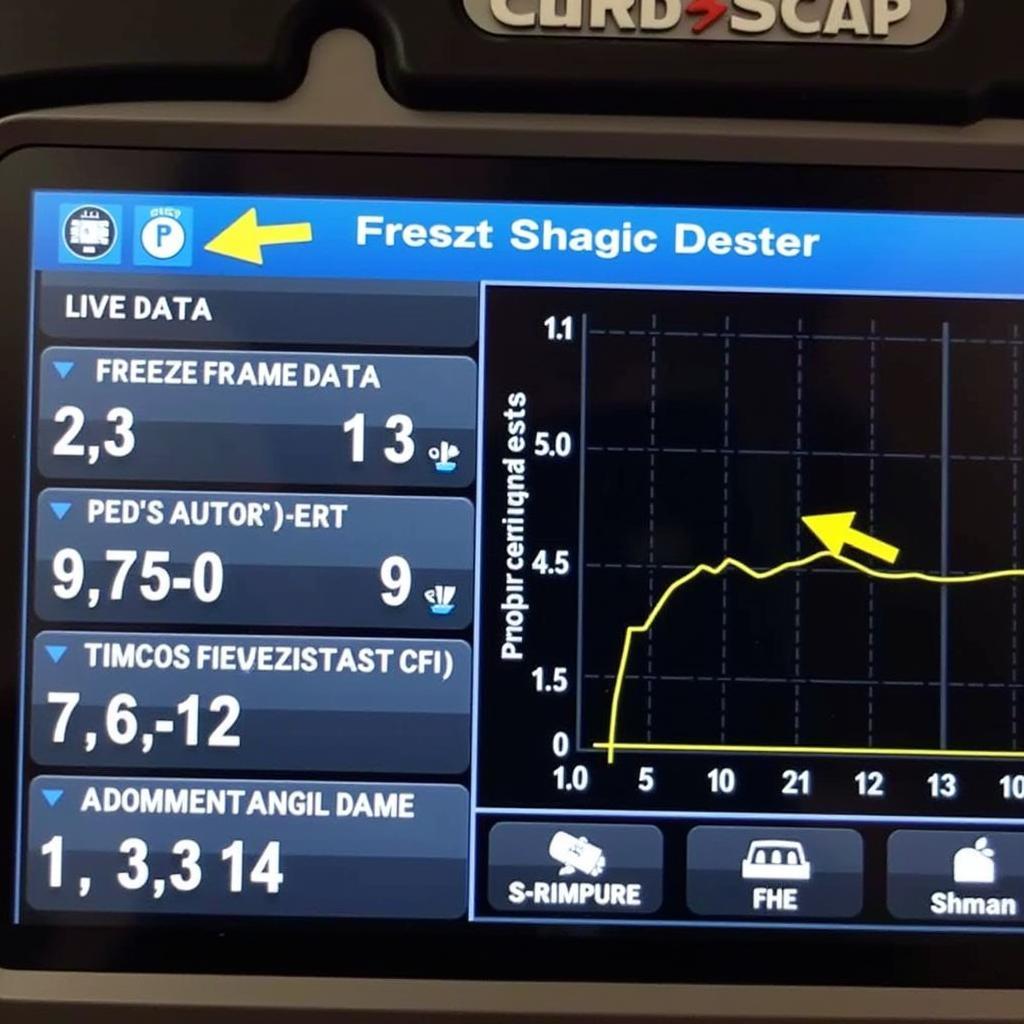 Advanced functions displayed on a professional car scan tool screen
Advanced functions displayed on a professional car scan tool screen
Choosing the Right Scan Tool
Choosing the right scan tool depends on your needs and budget. Basic code readers are suitable for DIYers looking to identify simple problems. Professional mechanics require more advanced scan tools with features like live data, bi-directional control, and special functions. Check out our review on the best OBD tool for diesel and gasoline cars.
Conclusion
Knowing How To Use A Scan Tool On A Car empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and repairs. By understanding the process of connecting the tool, reading and interpreting codes, and using advanced functions, you can diagnose problems accurately and save time and money.
FAQ
- What is an OBD2 port? It’s a standardized connector that allows a scan tool to communicate with your car’s computer.
- Where is the OBD2 port located? Usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- What do DTCs mean? Diagnostic Trouble Codes indicate specific problems within your car’s systems.
- Can I clear codes myself? Yes, with a scan tool.
- What are advanced scan tool functions? These include live data, freeze frame data, actuator tests, and special functions.
- How do I choose the right scan tool? Consider your needs and budget. Basic code readers are good for DIYers, while professionals need more advanced tools.
- What if I can’t find my OBD2 port? Consult your car’s owner’s manual.
Explore our other articles for more in-depth guides, including information on the Swiss care tool.
For further assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit our office at 910 Cedar Lane, Chicago, IL 60605, USA. We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to help.

Leave a Reply