On-board diagnostics, more commonly known as OBD, is an essential system built into modern vehicles to monitor and diagnose potential issues. This technology acts as your car’s internal communication network, relaying vital information about your engine, emissions, and other crucial components.
What is On-Board Diagnostics in a Car?
Essentially, OBD is a sophisticated computer system that continuously monitors your vehicle’s performance. It utilizes various sensors strategically placed throughout the engine and related systems. These sensors gather data in real-time, analyzing everything from engine speed and temperature to oxygen levels in the exhaust. If any of these readings deviate from the pre-programmed parameters set by the manufacturer, the OBD system illuminates the check engine light on your dashboard, alerting you to a potential problem.
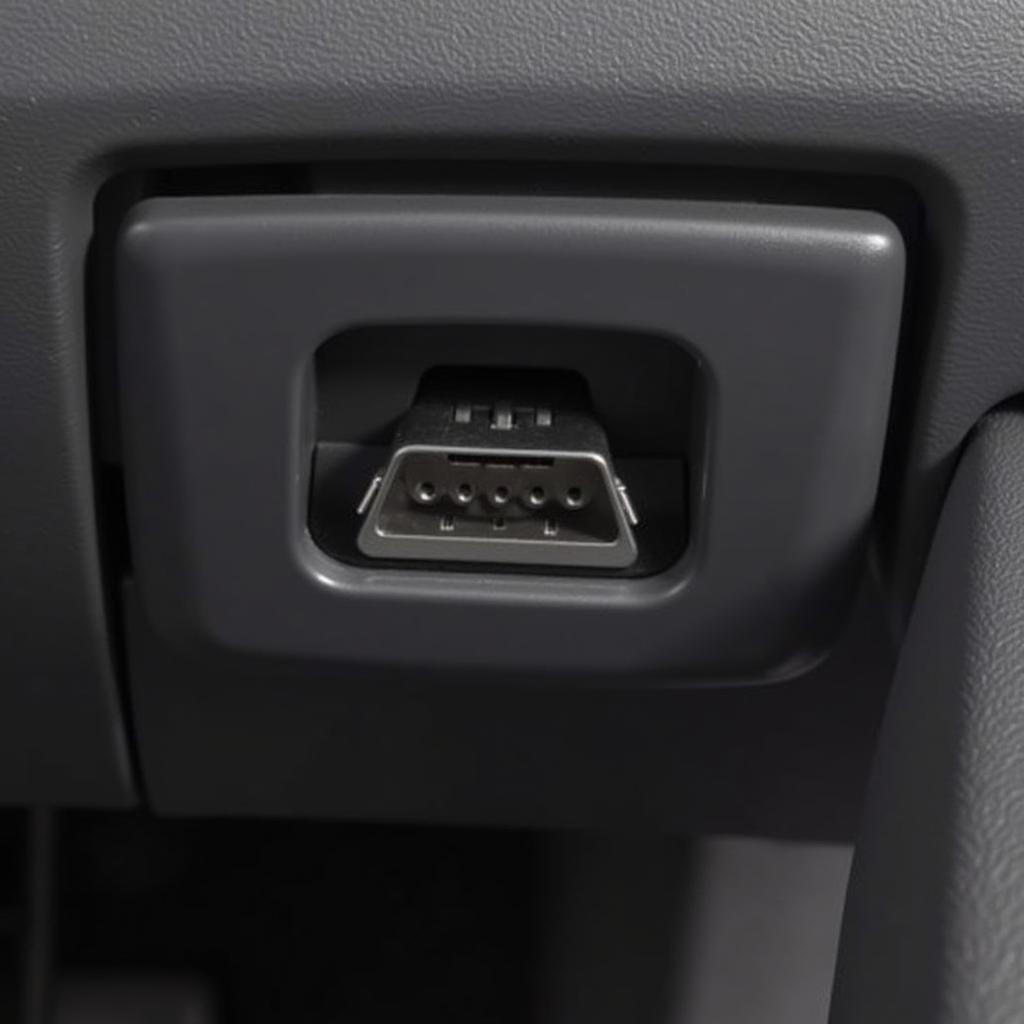 OBD Port Location
OBD Port Location
The Evolution of On-Board Diagnostics
The concept of on-board diagnostics emerged in the 1960s with rudimentary systems designed to monitor specific components. However, it wasn’t until the 1980s that OBD technology saw significant advancements. The introduction of OBD-I standardized the diagnostic process to some extent, but it was the arrival of OBD-II in the mid-1990s that revolutionized car diagnostics. OBD-II offered a universal connector, standardized diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and expanded monitoring capabilities to encompass emissions-related systems.
How On-Board Diagnostics Work
The OBD system functions as a continuous loop:
- Data Collection: Sensors throughout your vehicle collect information about various systems, including the engine, transmission, and emissions.
- Data Analysis: The OBD system’s computer, often referred to as the Engine Control Unit (ECU), analyzes the collected data against pre-set parameters.
- Fault Detection: If the data reveals any deviations from the norm, indicating a potential problem, the ECU stores a corresponding diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
- Alert System: The system alerts the driver by illuminating the check engine light on the dashboard.
- Data Retrieval: Mechanics or car owners can access the stored DTCs using an OBD-II scanner. This information helps pinpoint the source of the problem and guide repairs.
Benefits of On-Board Diagnostics
On-board diagnostics offer numerous benefits for both car owners and the automotive industry:
- Early Problem Detection: OBD systems can identify issues in their early stages, often before they escalate into major and costly repairs.
- Improved Repair Accuracy: DTCs provided by the OBD system help mechanics pinpoint the root cause of a problem, eliminating guesswork and unnecessary repairs.
- Enhanced Emissions Control: By monitoring emissions-related components, OBD systems contribute to lower vehicle emissions, benefiting the environment.
- Increased Vehicle Safety: OBD systems can detect issues with safety-critical systems, such as airbags and anti-lock brakes, potentially preventing accidents.
Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
When the OBD system detects an issue, it generates a specific DTC stored in the ECU’s memory. These codes follow a standardized format:
- First Character: Indicates the system related to the fault (e.g., “P” for Powertrain, “B” for Body, “C” for Chassis, “U” for Network).
- Second Character: Identifies whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Remaining Characters: Represent the specific fault within the system.
For instance, a DTC “P0301” would indicate a misfire detected in cylinder number one.
Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD2 reader NEXPeak NX301 Universal OBDII Car Diagnostic Scanner is a valuable tool that allows you to communicate with your vehicle’s OBD system and retrieve DTCs. These scanners vary in complexity and features, but even basic models can provide valuable information about your car’s health.
 OBD2 Scanner Display
OBD2 Scanner Display
Common On-Board Diagnostic Issues
While the check engine light can illuminate for various reasons, some common issues include:
- Loose Gas Cap: A loose or missing gas cap can trigger an emissions-related code.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: Oxygen sensors monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust to optimize engine performance and minimize emissions.
- Malfunctioning Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions, and a malfunction can significantly impact your vehicle’s emissions output.
- Spark Plug or Ignition Coil Problems: Issues with spark plugs or ignition coils can cause misfires, leading to reduced engine performance.
On-Board Diagnostics: Essential for Modern Car Maintenance
On-board diagnostics have become an indispensable part of modern car maintenance. Understanding how your car’s OBD system works empowers you to address minor issues before they become major problems and make informed decisions about your vehicle’s repair and maintenance.

Leave a Reply