Wound care nursing requires a specialized skill set and a collection of essential tools to provide effective and compassionate patient care. These tools help nurses assess, treat, and manage various wounds, ensuring optimal healing and minimizing patient discomfort.
Must-Have Tools for Every Wound Care Nurse
Wound care nurses utilize a variety of tools, from basic to advanced, to deliver comprehensive care. Understanding the purpose and application of each tool is crucial for providing effective treatment.
Assessment Tools: The Foundation of Wound Care
Accurate assessment is the cornerstone of effective wound care. These tools help nurses gather critical information about the wound’s characteristics:
- Ruler and Tape Measure: Precise measurements of wound length, width, and depth are essential for tracking progress and identifying potential complications.
- Wound Assessment Charts: Standardized charts help document wound characteristics, including location, size, tissue type, exudate, and surrounding skin condition.
- Photography: Visual documentation provides a clear record of the wound’s appearance over time, facilitating communication and evaluation of treatment effectiveness.
Cleaning and Debridement Tools: Preparing the Wound for Healing
Proper cleaning and debridement are crucial for removing debris, bacteria, and necrotic tissue, creating a healthy environment for healing:
- Saline Solution: Normal saline is the preferred solution for irrigating and cleansing wounds, minimizing tissue damage and promoting healing.
- Debridement Instruments: Specialized tools like scalpels, forceps, and curettes are used to remove dead or damaged tissue, facilitating the growth of healthy tissue.
- Wound Cleansers: Various wound cleansers are available, each designed for specific wound types and stages of healing.
Dressing and Bandaging Tools: Protecting and Supporting the Wound
Dressings and bandages protect the wound from further injury, absorb exudate, and create a moist environment that promotes healing:
- Primary Dressings: These dressings come into direct contact with the wound and are chosen based on the wound’s characteristics and stage of healing. Examples include alginates, hydrocolloids, and foams.
- Secondary Dressings: These dressings are placed over the primary dressing to provide additional absorption, protection, and support.
- Bandages and Tapes: These materials secure the dressings in place, preventing slippage and contamination.
- Compression Bandages: These specialized bandages apply pressure to the wound, helping to reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
Advanced Wound Care Tools and Techniques
As wound care technology advances, nurses are increasingly utilizing specialized tools and techniques to manage complex wounds.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): Enhancing Healing in Challenging Wounds
NPWT uses a vacuum-assisted closure device to create negative pressure within the wound bed, promoting granulation tissue formation and reducing edema.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): Boosting Oxygen Delivery to Promote Healing
HBOT involves exposing the patient to 100% oxygen at higher-than-normal atmospheric pressure, increasing the amount of oxygen dissolved in the blood and tissues, promoting wound healing.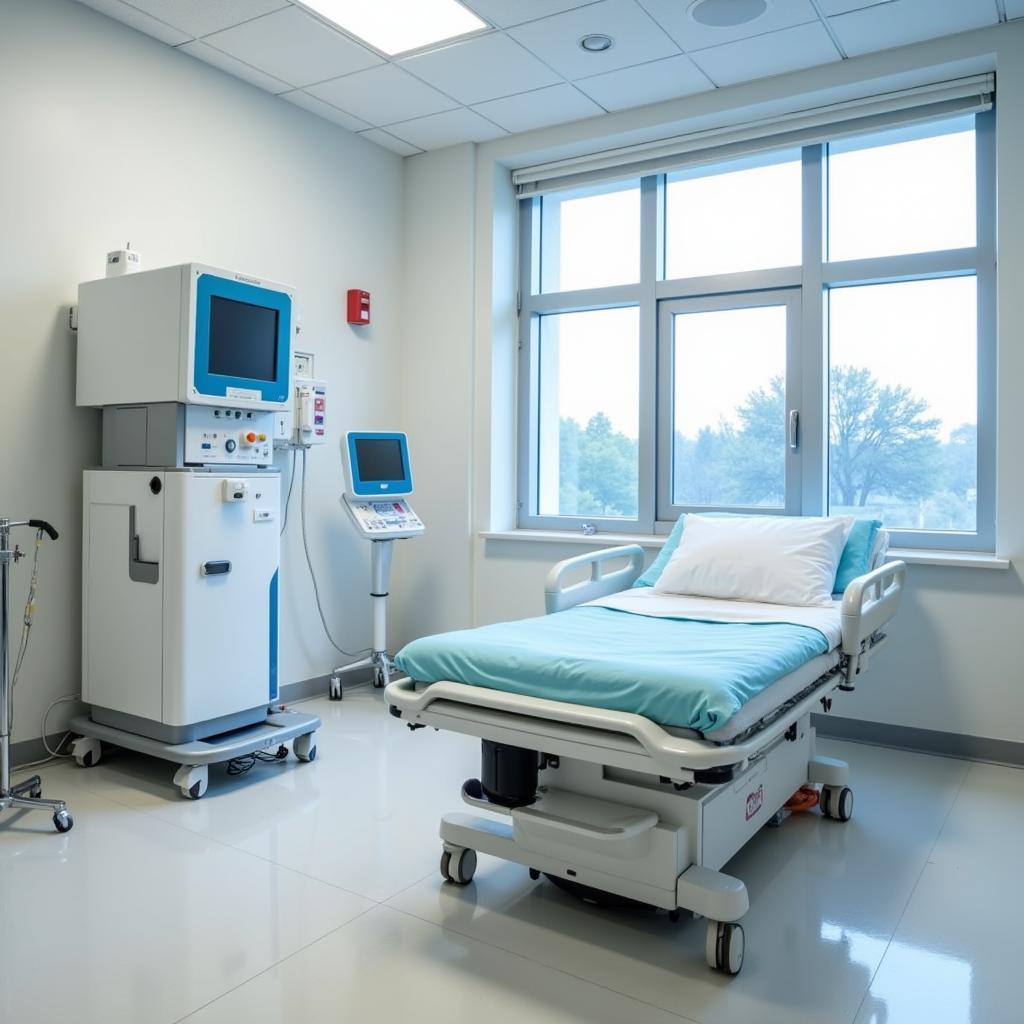  Advanced Wound Care: NPWT and HBOT machines.
Advanced Wound Care: NPWT and HBOT machines.
Conclusion: The Right Tools for Optimal Wound Healing
Wound care nurses play a critical role in promoting wound healing and improving patient outcomes. By utilizing the right tools and techniques, wound care nurses can ensure that patients receive the best possible care. Effective wound care requires a comprehensive understanding of wound assessment, cleaning, debridement, and dressing techniques, as well as the appropriate use of advanced tools and technologies.
FAQs
- What is the most important tool for a wound care nurse? Accurate assessment is crucial, making assessment tools like rulers, charts, and photography vital.
- How often should dressings be changed? Dressing frequency depends on the wound type and the specific dressing used, ranging from daily to weekly.
- What is the purpose of debridement? Debridement removes dead tissue, promoting healthy tissue growth and preventing infection.
- What are the benefits of NPWT? NPWT helps reduce edema, promote granulation tissue formation, and enhance healing in complex wounds.
- How does HBOT promote wound healing? HBOT increases oxygen delivery to the wound, stimulating cell growth and tissue repair.
- What are some common wound care challenges? Challenges include managing infection, promoting healing in chronic wounds, and addressing patient pain and discomfort.
- Where can I find more information on wound care? Resources include professional organizations, medical journals, and online educational platforms.
Need assistance? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 910 Cedar Lane, Chicago, IL 60605, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.